Waste Hierarchy- The Inverted Pyramid
What is the Inverted Pyramid?
The inverted pyramid that shows the most important areas of sustainability at the top, with the least important at the bottom. The hierarchy allows us analyse our relationship with waste and how we can effectively tackle the battle in a sustainable way.
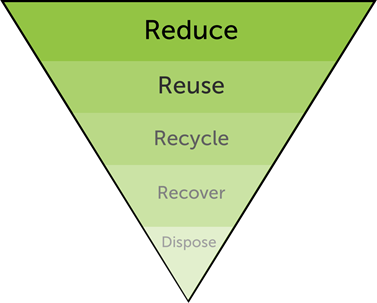
This pyramid is used to show how we tackle waste, as shown in the diagram above, Reduce is the most crucial way to tackle the global waste problem. In contrast at the bottom of the pyramid we have Dispose which is the least productive way to fight waste. By disposing of waste without much thought it can cause more harm than good as there are certain goods that need to be disposed of correctly, if not they can be harmful to the environment.
Components of the Inverted Pyramid
Let’s take a look into the key components of the pyramid in more detail to gain a better understanding of how this approach will tackle the fight against waste.
Reduce
The concept of Reduce is to reduce the amount of non-sustainable materials used in products by finding alternatives. For example, using paper bags instead of plastic bags and finding “green” alternatives to key materials used to create products.
Reuse
Reuse means using second- and rather than going straight to new items. An example is buying second-hand clothing instead of new, by doing this you are using products that have already been manufactured. By re-using items, it allows for be less wastage forced out into the environment as well as it being a cheaper alternative in the majority of cases
Recycle
Recycling is turning old products into something brand new. In our sector, it means taking the metals out of your mobile phones so that they can be used for making new products. There is a slight downfall to this as this component does use a lot of energy which is why Reuse is the preferred option.
Recover
Recover is associated with energy recovery. It means turning waste into energy such as burning biomass to create heat. This is something Re-Tek stand by as we have a Biomass Boiler which heats the whole facility. As well as making the use of solar panels to create energy to power the facility.
Dispose
The last area that we want to avoid at all costs, disposal means putting waste into the ground in landfill. It should only occur when all other options have been exhausted and there is no other way.
Waste Hierarchy and the Circular Economy
The two go hand in hand as they are both models that have the outcome to be beneficial to our environment. They both have the objective to reduce the overall waste output. The Circular Economy has the main goal to extend a product’s lifecycle, and to keep it in the economy for longer. This is done by finding alternatives to immediate dispose after it is no longer needed by someone or a business.
The diagram below shows the difference between how the Linear Economy model compares to the Circular Economy model.
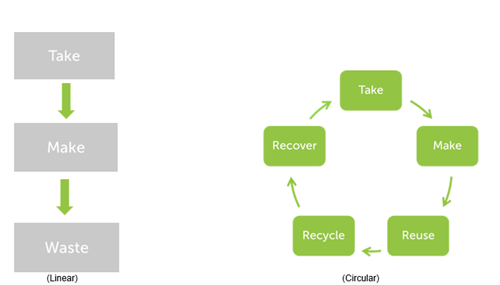
As a society, we currently, generally operate within the Linear Economy, we are trying to move towards the Circular Economy as a whole, as we are realising the positive potential it has in some aspect of the supply chain throughout all industries.


